Inter-VLAN Routing can be defined as a way to forward traffic between different VLANs by implementing a router in the network. VLANs logically segment the switch into different subnets, when a router is connected to the switch, an administrator can configure the router to forward the traffic between the various VLANs forwards traffic to the router which then forwards the traffic to the destination network regardless of the VLAN configured on the switch.
Download Free CCNA Android Apps from Playstore
Table of Contents
There are two ways in which inter-VLAN routing can be accomplished.
Traditional inter-VLAN routing
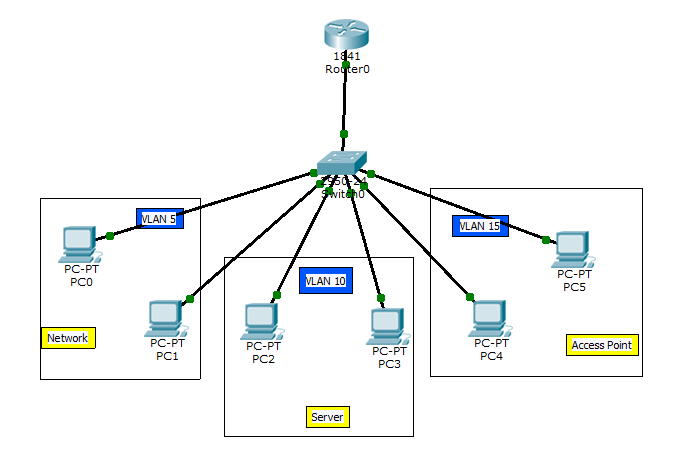
Router-on-a-stick
Traditional inter-VLAN routing
In this type of inter-VLAN routing, a router is usually connected to the switch using multiple interfaces, one for each VLAN. The interface on the router is configured as the default gateway for the VLANs configured on the switch the ports that connect to the router from the switch are configured in access mode in their corresponding VLANs.
When a user node sends a message to a user connected to a different VLAN, the message moves from their node to the access port that connects to the router on their VLAN. When the router receives the packets, it examines the packet’s destination IP address and forwards it to the correct network using the access port for the destination VLAN. The switch now can forward the frame to the destination node since the router changed the VLAN information from the source VLAN to the destination VLAN.
In this form of inter-VLAN routing, the router has to have as many LAN interfaces as the number of VLANs configured on the switch. Therefore, if a switch has 10 VLANs, the router should have the same number of LAN interfaces.
What is VLAN | How to Configure VLAN (Access and Trunk)
Inter-VLAN routing using router-on-a-stick
In Inter-VLAN routing using Router-on-a-stick, the router is connected to the switch using a single interface. The switch port connecting to the router is configured as a trunk link. The single interface on the router is then configured with multiple IP addresses that correspond to the VLANs on the switch. This interface accepts traffic from all the VLANs and determines the destination network based on the source and destination IP in the packets. It then forwards the data to the switch with the correct VLAN information.
In this type of inter-VLAN routing, the interface connecting the router to the switch is usually a trunk link. The router accepts traffic that is tagged from the VLANs on the switch through the trunk link. On the router, the physical interface is divided into a smaller interfaces called sub-interfaces. When the router receives the tagged traffic, it forwards the traffic out to the sub-interface that has the destination IP address. Sub-interfaces aren’t real interfaces but they use the LAN physical interfaces on the router to forward data to various VLANs. Each sub-interfaces is configured with an IP address and assigned a VLAN based on the design.
<==Access CCNA LAB’s for Free==>
Learn English with Hindi, Marathi, Urdu translation