Typically LAN connection is used within the company and WAN allows you to connect to remote locations, With WAN you don’t own infrastructure for WAN connection, another company, such as a telephone company, cable provider provides the infrastructure. WAN connections are usually slower than LAN connections.
WAN normally works at layer 2 of the OSI model.
DCE terminates a connection between sites and provides clocking and synchronization for that connection; it connects to a DTE
DCE category includes equipment such as CSU/DSU (Channel service unit/ data service unit), Network terminator type 1(NT1), and cable and analog modems. A DTE is an end-user device, such as a router or pc which connects to the WAN via DCE
CSU/DSU terminates digital/synchronous circuits and modem terminates analog/synchronous circuits.
Download Free CCNA Android Apps from Playstore
Table of Contents
Connection types
1) Leased line connections
Basically, it is a dedicated circuit connection between two sites. It simulates a single cable connection between the remote and local site
A leased-line is best suited when both of these conditions hold:
– The distance between the two sites is small, making the leased line cost-effective
– A constant amount of traffic occurs between two sites and you need to guarantee bandwidth for certain applications
Even though the leased line can provide guaranteed bandwidth and minimal delay for connection, other available solutions also can provide the same, the main disadvantage of a leased line is their cost – they are typically a most expensive WAN solution, each connection will need a separate interface on your router, leased line use synchronous serial connection data rates is from 2400bps to 45Mbps.
The synchronous connection allows you to send and receive information simultaneously without having to wait for any signal from the remote side, the synchronous connection does not need to indicate when it is beginning to send something or the end of the transmission. These two things plus how clocking is done are three major differences between synchronous and asynchronous connections, asynchronous connections are typically used for dialup connections such as modems.
If you purchased a leased line you will need the following equipment:
DTE: A router with a synchronous serial interface
DCE: A CSU/DSU to terminate the carrier’s leased line connection
Best Book To Learn CCNA – Crack Cisco Certification & Crack Interviews
Best Book To Learn Python – Path to Success in Programming
2) Circuit switched connection
These are dial-up connections, like those that are used by a pc with a modem when dialing up an ISP.
Circuit-switched includes the following types
Asynchronous serial connection – This includes analog modem dial-up connections
Synchronous serial connection: These includes digital ISDN, BRI, and PRI dialup connections; they provide guaranteed bandwidth
Asynchronous is the cheapest form of WAN services but are also the slowest and most unreliable of the services, FCC (federal communications commission) restrict analog data rate to 53Mbps, the main problem of circuit-switched is that they are expensive if you need to make connections over a longer distance, with a per-minute charge that varies, depending on the destination: the more data you have to send, more time it will take, more money you will have to pay.
If you will be using the circuit-switched analog connection, you will need this equipment :
DTE: A router with asynchronous serial interface
DCE: A modem
If you will be using a circuit-switched digital connection, you will need this equipment
DTE: A router with an ISDN interface
DCE: An NT1 for a BRI or a CSU/DSU for PRI
Check Out the Headphones – 50% to 70% Off
Check Out the Earbuds – 50% to 70% Off
Check Out The LAB Configuration eBook – Class A, Class B, Class C, MiN worth $78 Get at $18
3) Packet switched connection
With a leased line and circuit-switched connections, a physical circuit is used to make the connection between two sites. With a leased line, the same circuit path is always used, with the circuit-switched path is built every time a phone call is made, making it highly probable that the same circuit path will not be used for every phone call, the packet-switched connection uses a logical circuit to make connections between two sites. These logical circuits are referred to as virtual circuits (VCs)
One advantage of a logical circuit over a physical one is that a logical circuit is not tied to any particular physical circuit. Instead, a logical circuit is built across any available physical connection. Another advantage of a logical circuit is you can build many logical circuits over the same physical circuit.
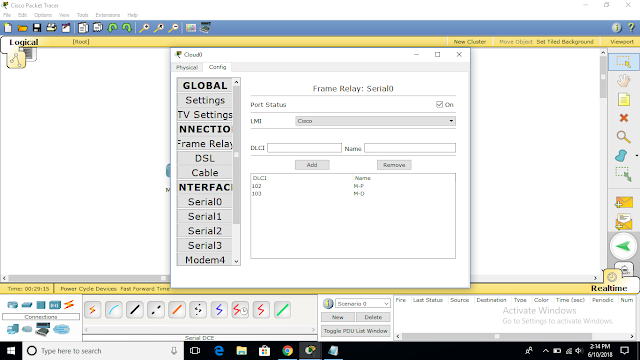
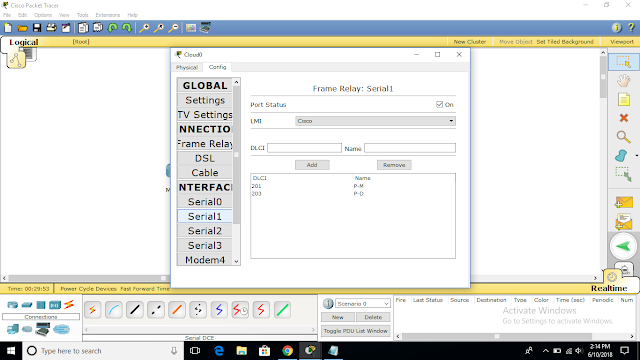
Technologies that use packet switching and logical circuits include ATM (asynchronous transfer mode), frame-relay, X.25.
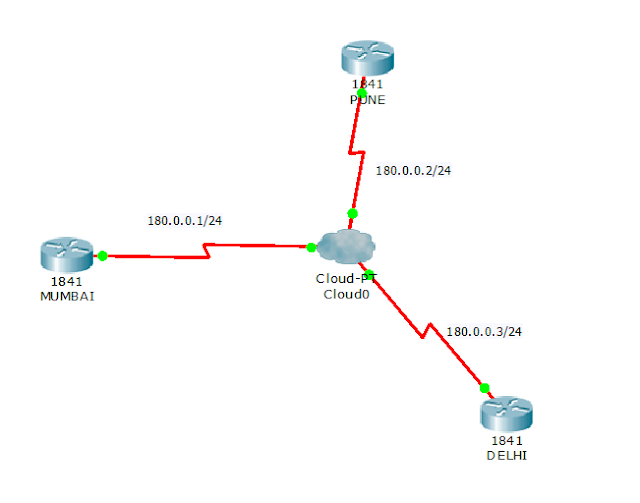
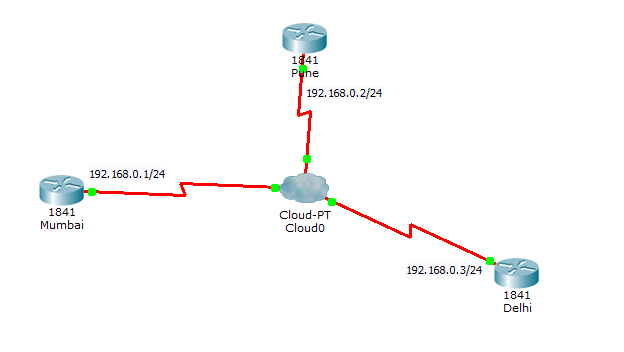
On Router1 (Mumbai)
Router>en
Router#conf t
Router(config)#hostname MUMBAI
MUMBAI(config)#int s
MUMBAI(config)#int serial 0/0/0
MUMBAI(config-if)#encapsulation frame-relay
MUMBAI(config-if)#ip address 180.0.0.1 255.255.255.0
MUMBAI(config-if)#cl ra 64000
MUMBAI(config-if)#no sh
PUNE(config-if)#^Z
PUNE#wr
On Router2 (Pune)
Router>en
Router#conf t
Router(config)#hostname PUNE
PUNE(config)#int serial 0/0/0
PUNE(config-if)#encapsulation frame-relay
PUNE(config-if)#ip address 180.0.0.2 255.255.255.0
PUNE(config-if)#cl ra 64000
PUNE(config-if)#no sh
PUNE(config-if)#^Z
PUNE#wr
On Router3 (Delhi)
Router>en
Router#conf t
Router(config)#hostname DELHi
DELHI(config)#int serial 0/0/0
DELHI(config-if)#encapsulation frame-relay
DELHI(config-if)#ip address 180.0.0.3 255.255.255.0
DELHI(config-if)#cl ra 64000
DELHI(config-if)#no sh
DELHI(config-if)#^Z
DELHI#wr



<==Access CCNA LAB’s for Free==>